- Home
- Product >
PRODUCT CATEGORY
RECOMMENDED PRODUCTS
〇 Brand laser cutting head


〇 Laser Nozzle
〇 Protective Window Lens
〇 Laser Ceramic
〇 Focus & Colliminating Lens
〇 Lens Seat & Seal Ring
〇 Capacitive Sensor
〇 FSCUT/Friendess Control Series
28mm H15 Normal Single/Double
Raytools BT240S
〇 Handheld box
- Consumables >
PRODUCT CATEGORY
RECOMMENDED PRODUCTS
〇 Cleaning Kits



〇 Disassembly tools
〇 Filter Element
〇 Dust Cover
〇 CLARIANT antifrogen N
〇 EUBO lubricating oil
〇 Fiber Lasers
〇 Optical fiber protective cap
Cleaning Kits 10 Inch PP Cotton Filter Element
〇 Laser goggles
〇 Spare Parts For YAG
- Service support >
Electrical circuit repair
Focus collimator replacement
Laser cutting head maintenance
Cavity cleaning Crystal repair
Cutting equipment Laser repair
Laser sensor handheld box repair
- Panso Infos >
Laser Encyclopedia
Job Offers
- About us
- Contact us
With the rapid development and wide application of laser technology, more and more laser products have appeared in our living environment. As a practitioner in the laser field, there are more opportunities to be exposed to laser and related products. However, laser products on the market today are good and bad. Some laser products can be used safely, but some improper use can cause damage to our eyes and skin, and even cause serious hazards such as fire, electric shock, and burns. Especially in the hot summer weather, frequent rainfall and humid environment, it is easy to cause condensation inside the laser, thereby reducing the performance of the laser or even damage. So how can everyone know whether a laser product is safe? Let the editor tell you!
First of all, when we use a laser, we should first pay attention to its classification information. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) respectively classify lasers according to the laser output value:
The IEC standard divides laser equipment into four classes, namely Class1, Class2, Class3, and Class4. Which can be subdivided into the following levels:
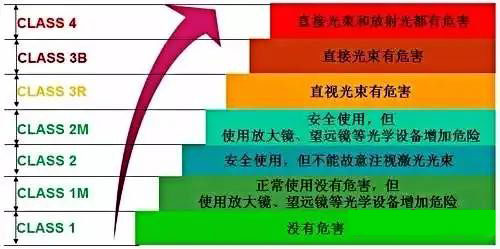
For example, Class1 laser equipment is a kind of safety equipment under "foreseeable working conditions"; while Class4 laser equipment is equipment that may generate harmful diffuse reflections, which can cause skin burns and even fires. Be especially careful. The FDA standard divides laser equipment into five classes, namely Class I to Class IV. Class I laser products have no biological hazards. Any beam that may be viewed is shielded, and the laser system is interlocked during laser exposure. The output power of Class II laser products is 1 milliwatt. Will not burn the skin and cause fire. Because eye reflection can prevent some eye damage, this type of laser is not considered a dangerous optical device. Class IIIa laser products have an output power of 1 mW to 5 mW. Will not burn the skin. Under certain conditions, this type of laser can cause blindness and other damage to the eyes. Class IIIb laser products have an output power of 5 mW to 500 mW. When the power is relatively high, such laser products can scorch the skin. This type of laser product is clearly defined as harmful to the eyes, especially when the power is relatively high, it will cause eye damage. The output power of Class IV laser products is greater than 500 milliwatts. Such laser products must be able to cause eye damage. Just like burning the skin and lighting clothing, it can also ignite other materials. The safety level of formal laser equipment should be marked in accordance with FDA or IEC standards or other laser product specifications. We can use these lasers reasonably according to the label. Taking the IEC standard as an example, laser products for children’s toys must meet Class 1 requirements; and products that can be accessed or used by ordinary consumers, such as laser pointers, laser measuring equipment, and tool equipment with laser instructions, are generally classified as Class 2. Not higher than Class 3R. So what protective measures should we take for each level of laser? Still taking the IEC standard as an example, it is now listed here for everyone.
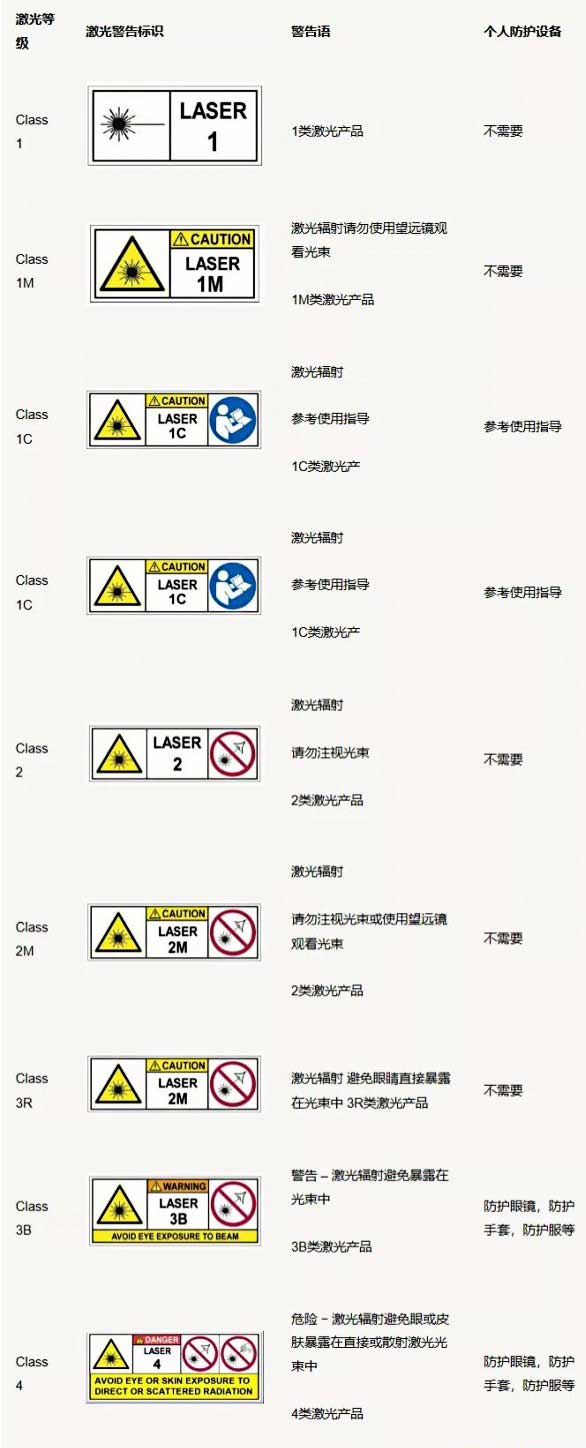
Of course, during the R&D and debugging process of our laser practitioners, sometimes due to system changes or component disassembly, it is impossible to determine the laser level of a certain part of the product. At this time, we cannot arbitrarily assume that its level is the same as the laser source level due to trouble, or treat it at a very low level; on the contrary, we generally have to assume that it is Class 3B or even Class 4, and take adequate safety protection measures. For example, wear laser protective glasses, protective gloves, etc., and operate by someone who has received laser safety training to avoid accidents.
In addition, laser practitioners should also pay attention to the following points when using laser products:
1. Before the first operation, read the instruction manual and operation manual attached to the laser product in detail, and strictly abide by the specified operation process.
2. Do not look directly at the laser beam and its reverse beam. When the machine fails, even if there is no visible light, you should not approach the laser for inspection, because some lasers emit infrared and ultraviolet light invisible to the human eye.
3. When using Class 3B and above lasers, the staff should remove any objects with shiny surfaces, such as ornaments, watches and badges. And wear protective glasses to prevent the reflected light from entering the eyes and causing damage. Long hair should be tied up and a lab cap should be worn. If you use laser cutting equipment to process dust-prone materials, you should wear a dust mask and do a good job of fire prevention.
4. The peak power of the pulsed (Q-switched, mode-locked, ultra-fast) laser is extremely high, which may cause damage to the experimental components. Please confirm the damage resistance threshold of your experimental parts before use.
5. In the working area where the laser equipment is located, there should be no flammable and explosive materials. When the equipment is working, the staff should not leave for a long time.
6. Regularly maintain and overhaul the laser equipment, and keep the room and around the laser equipment clean and tidy and free of grease.
7. When staff find abnormalities during processing, they should stop the machine immediately, troubleshoot the fault or report to the supervisor in time.
Of course, applications in the laser field are ever-changing, and there are also many types of laser products we encounter daily. What is listed here is only the general content of laser product safety matters, and please handle it flexibly according to the specific situation. I hope that every laser practitioner can protect himself and contribute to the laser industry in the "post-epidemic era"!


Product
Sales Manager:Roy Ren
ADD: Xingyu Science Park, No. 688, Chunshen Road, High tech Zone, Jinan City, Shandong Province CHINA
E-mail:roy370124@gmail.com
Tel:+86 150 9898 4876
whatsapp: +86 86 150 9898 4876



